[오늘의 일지]
트랙학습 녹화 강의 - Object Detection(One-Stage Detection)
[상세 내용]
Object Detection(One-Stage Detection)
- One-Stage Detection은 객체 감지(Object Detection) 작업을 수행하는 딥러닝 모델 아키텍처 중 하나로, 객체의 위치와 클래스를 한 번에 예측하는 방식입니다. 이러한 모델은 여러 개의 bounding box와 클래스 확률을 한 번에 예측하며, 여러 객체가 한 이미지 내에 존재하는 경우에도 효과적으로 처리할 수 있습니다. 대표적인 One-Stage Detection 모델로는 YOLO (You Only Look Once)와 SSD (Single Shot Multibox Detector)가 있습니다. 제가 들은 수업에서는 YOLO1 모델을 활용해서 실습을 하였습니다.
원리
- 원리는 이름 그대로 한 가지 단계에 의해서 이루어져 있습니다. 아래의 그림에서 아래에 있는 모델이 One-Stage Detection 모델의 대표적인 과정을 보여주는 그림입니다.
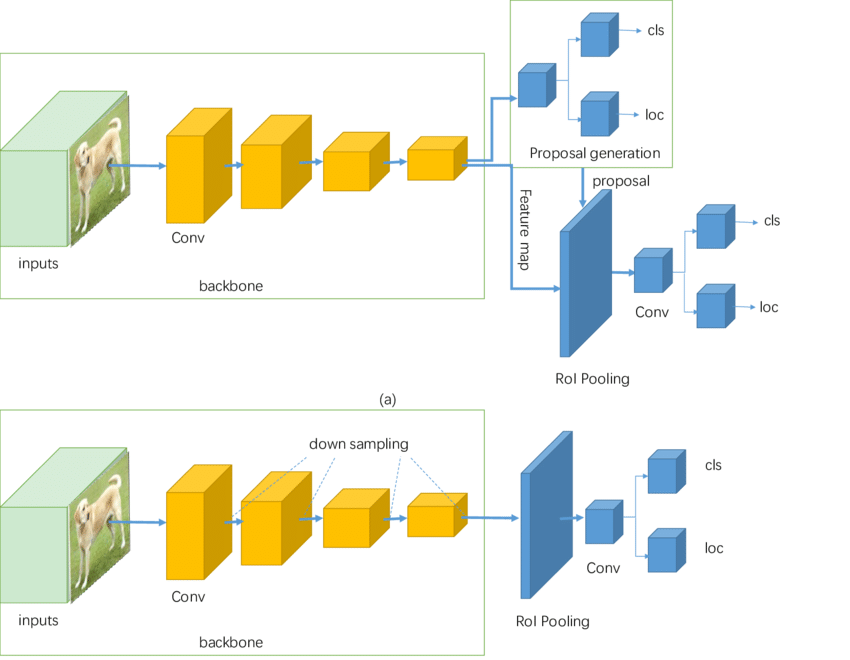
특징
Grid 기반의 예측
- 입력 이미지를 격자(grid)로 나누어 각 격자 셀에 대해 bounding box와 클래스에 대한 예측을 수행합니다.
- YOLO에서는 이미지를 SxS 크기의 격자로 나누고, 각 격자 셀은 B개의 bounding box 예측을 담당합니다.
- SSD에서는 각 격자 셀마다 다양한 크기와 종횡비를 가진 prior box를 사용하여 예측합니다.
Anchor Boxes (Prior Boxes)
- 모델이 예측할 bounding box의 후보를 나타내는 anchor boxes를 사용합니다. 각 anchor box는 다양한 크기와 종횡비를 가지며, 격자 셀마다 다른 anchor boxes를 사용합니다.
- 예측된 bounding box는 anchor box를 기준으로 위치를 조정하고, 클래스를 예측합니다.
다중 스케일의 특징 맵 활용
- 다양한 객체 크기를 처리하기 위해 입력 이미지를 여러 다른 스케일의 특징 맵으로 변환합니다.
- 예를 들면 YOLO는 특정 스케일의 특징 맵에서 bounding box 예측을 수행하고, SSD는 여러 스케일의 특징 맵에서 각기 다른 크기의 객체를 예측합니다.
손실 함수 (Loss Function)
- 모델의 학습을 위해 정답과의 차이를 계산하는 손실 함수를 정의합니다.
- 일반적으로 bounding box 위치를 조정하는 부분과 객체의 클래스를 분류하는 부분으로 나누어 손실을 계산합니다.
Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
- 여러 bounding box 예측이 겹치는 경우, NMS를 사용하여 가장 확률이 높은 예측을 선택하고, 겹치는 예측을 제거합니다.
- 이번에 실습에서 사용한 YOLO 1은 Anchor Boxes가 도입되기 전 모델이라 NMS의 효과가 크지 않았습니다.
모델 코드 예시
- YOLO 1 모델을 사용하였습니다.
class YOLOv1_RESNET(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super().__init__()
num_classes = num_classes
num_bboxes = 2
grid_size = 7
resnet18 = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
layers = [m for m in resnet18.children()]
self.backbone = nn.Sequential(*layers[:-2])
self.head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=1, padding=0,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=(4+1)*num_bboxes+num_classes, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(grid_size, grid_size))
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.backbone(x)
out = self.head(out)
return out
- YOLO 1 LOSS 구현
def build_target_grid(target):
target_grid = torch.zeros((1+4+num_classes, grid_size, grid_size), device=device)
for gt in target:
xc, yc, w, h, cls_id = gt
xn = (xc % (1/grid_size))
yn = (yc % (1/grid_size))
cls_id = int(cls_id)
i_grid = int(xc * grid_size)
j_grid = int(yc * grid_size)
target_grid[0, j_grid, i_grid] = 1
target_grid[1:5, j_grid, i_grid] = torch.Tensor([xn,yn,w,h])
target_grid[5+cls_id, j_grid, i_grid] = 1
return target_grid
class YOLOv1_LOSS():
def __init__(self, num_classes, device, lambda_coord=5., lambda_noobj=0.5):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.device = device
self.grid_size = 7
self.lambda_coord = lambda_coord
self.lambda_noobj = lambda_noobj
self.mse_loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction="sum")
def __call__(self, predictions, targets):
self.batch_size, _, _, _ = predictions.shape
groundtruths = self.build_batch_target_grid(targets)
groundtruths = groundtruths.to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
iou1 = self.get_IoU(predictions[:, 1:5, ...], groundtruths[:, 1:5, ...])
iou2 = self.get_IoU(predictions[:, 6:10, ...], groundtruths[:, 1:5, ...])
ious = torch.stack([iou1, iou2], dim=1)
max_iou, best_box = ious.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_iou = torch.cat([max_iou, max_iou], dim=1)
best_box = torch.cat([best_box.eq(0), best_box.eq(1)], dim=1)
predictions_ = predictions[:, :5*2, ...].reshape(self.batch_size, 2, 5, self.grid_size, self.grid_size)
obj_pred = predictions_[:, :, 0, ...]
xy_pred = predictions_[:, :, 1:3, ...]
wh_pred = predictions_[:, :, 3:5, ...]
cls_pred = predictions[:, 5*2:, ...]
groundtruths_ = groundtruths[:, :5, ...].reshape(self.batch_size, 1, 5, self.grid_size, self.grid_size)
obj_target = groundtruths_[:, :, 0, ...]
xy_target = groundtruths_[:, :, 1:3, ...]
wh_target= groundtruths_[:, :, 3:5, ...]
cls_target = groundtruths[:, 5:, ...]
positive = obj_target * best_box
obj_loss = self.mse_loss(positive * obj_pred, positive * ious)
noobj_loss = self.mse_loss((1 - positive) * obj_pred, ious*0)
xy_loss = self.mse_loss(positive.unsqueeze(dim=2) * xy_pred, positive.unsqueeze(dim=2) * xy_target)
wh_loss = self.mse_loss(positive.unsqueeze(dim=2) * (wh_pred.sign() * (wh_pred.abs() + 1e-8).sqrt()),
positive.unsqueeze(dim=2) * (wh_target + 1e-8).sqrt())
cls_loss = self.mse_loss(obj_target * cls_pred, cls_target)
obj_loss /= self.batch_size
noobj_loss /= self.batch_size
bbox_loss = (xy_loss+wh_loss) / self.batch_size
cls_loss /= self.batch_size
total_loss = obj_loss + self.lambda_noobj*noobj_loss + self.lambda_coord*bbox_loss + cls_loss
return total_loss, (obj_loss.item(), noobj_loss.item(), bbox_loss.item(), cls_loss.item())
def build_target_grid(self, target):
target_grid = torch.zeros((1+4+self.num_classes, self.grid_size, self.grid_size), device=self.device)
for gt in target:
xc, yc, w, h, cls_id = gt
xn = (xc % (1/self.grid_size))
yn = (yc % (1/self.grid_size))
cls_id = int(cls_id)
i_grid = int(xc * self.grid_size)
j_grid = int(yc * self.grid_size)
target_grid[0, j_grid, i_grid] = 1
target_grid[1:5, j_grid, i_grid] = torch.Tensor([xn,yn,w,h])
target_grid[5+cls_id, j_grid, i_grid] = 1
return target_grid
def build_batch_target_grid(self, targets):
target_grid_batch = torch.stack([self.build_target_grid(target) for target in targets], dim=0)
return target_grid_batch
def get_IoU(self, cbox1, cbox2):
box1 = self.xywh_to_xyxy(cbox1)
box2 = self.xywh_to_xyxy(cbox2)
x1 = torch.max(box1[:, 0, ...], box2[:, 0, ...])
y1 = torch.max(box1[:, 1, ...], box2[:, 1, ...])
x2 = torch.min(box1[:, 2, ...], box2[:, 2, ...])
y2 = torch.min(box1[:, 3, ...], box2[:, 3, ...])
intersection = (x2-x1).clamp(min=0) * (y2-y1).clamp(min=0)
union = abs(cbox1[:, 2, ...]*cbox1[:, 3, ...]) + \
abs(cbox2[:, 2, ...]*cbox2[:, 3, ...]) - intersection
intersection[intersection.gt(0)] = intersection[intersection.gt(0)] / union[intersection.gt(0)]
return intersection
def generate_xy_normed_grid(self):
y_offset, x_offset = torch.meshgrid(torch.arange(self.grid_size), torch.arange(self.grid_size))
xy_grid = torch.stack([x_offset, y_offset], dim=0)
xy_normed_grid = xy_grid / self.grid_size
return xy_normed_grid.to(self.device)
def xywh_to_xyxy(self, bboxes):
xy_normed_grid = self.generate_xy_normed_grid()
xcyc = bboxes[:,0:2,...] + xy_normed_grid.tile(self.batch_size, 1,1,1)
wh = bboxes[:,2:4,...]
x1y1 = xcyc - (wh/2)
x2y2 = xcyc + (wh/2)
return torch.cat([x1y1, x2y2], dim=1)
[마무리]
오늘은 Object Detection 중에 One-Stage Detection 모델에 대해서 알아보고 초기 모델이라고 할 수 있는 YOLO 1 모델을 활용해서 실습을 해보는 수업을 들었습니다. 아직까지는 빠르게 실습을 하고 결과를 강의를 통해 확인하면서 진도를 따라가기 바쁘지만 추후에 프로젝트나 다른 데이터를 통해서 사용하다 보면 발전이 있을 거라고 믿습니다.
'AI > 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AI 부트캠프] DAY 98 - 트랙학습 CV 12 (0) | 2023.12.08 |
|---|---|
| [AI 부트캠프] DAY 97 - 트랙학습 CV 11 (1) | 2023.12.07 |
| [AI 부트캠프] DAY 95 - 트랙학습 CV 9 (1) | 2023.12.05 |
| [AI 부트캠프] DAY 94 - 트랙학습 CV 8 (0) | 2023.12.02 |
| [AI 부트캠프] DAY 93 - 트랙학습 CV 7 (1) | 2023.12.01 |




댓글